[vc_row][vc_column][vc_column_text css=”.vc_custom_1582780572406{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
What Does Collaborative Robot Mean? Everything You Need to Know About Cobots
Back in the late 18th century, the First Industrial Revolution was a game-changer for manufacturers and factories. Since then, manufacturing processes and factories have taken advantage of both machines and manpower to maximize productivity. Over time, manufacturers have adapted to the latest technology made to make production faster or more effective and safer to the manpower on the work floor.
And at this day and age of smart technology, AI, and more, manufacturing companies are now welcoming the next big thing for efficient production. Enter: collaborative robots, or cobots. Here’s what you need to know about collaborative robots and what they can do for your production.
What Does Collaborative Robot Mean?
Simply put, collaborative robots are robots that can safely work alongside and with a human. While there are some machines already in manufacturing that require humans for it to operate, cobots interact with a human and work alongside the same step of their production.
Another difference is that collaborative robots are built for safety, so the chances of workplace hazards while interacting with cobots is relatively low. The Bureau of Labor Statistics lists 23.5 percent of non-fatal injuries coming from contact with equipment. Collaborative robots are built to reduce the risk of that in the workplace based on how it’s built and operated.
Collaborative robots are made with lightweight materials and constructed to have rounded edges. These can avoid and accidental injuries while handling these robots in the workplace. To make it safer, cobots have a speed and force limit when moving and have sensors to determine key safety features.
Because of their safety features, people in manufacturing can operate directly with cobots rather than the former safety measure of locking robots in cages or rooms to operate to ensure no one gets hurt by their weight or fast movements.
Around five percent of global industrial robot sales are cobots. In 2018, around 14,000 cobots were installed in various industrial centers; in 2017, this was only 11,000. This may not seem like a lot on a global scale, but the industry was valued at $580 million and expected to reach near the tens of billions by 2024. But for now, that means collaborative robots account for roughly five percent of industrial robots all around the world. Given the increase, the demand is expected to rise in 2019 and 2020.
Collaborative Robot Origins
Collaborative robots were invented in 1996 due to an initiative that began two years earlier. In 1994, Prasad Akella of the General Motors Robotics Center, later with a General Motors Foundation research grant in 1995, wanted to find a way to make robots and people work safely together. The first collaborative robot was invented in 1996 by Northwestern University professors J. Edward Colgate and Michael Peshkin and patented a year later.
The first collaborative robot had no internal power source that could move on its own. To make it safe, it was the human that had control over its power. Back then, it wasn’t called collaborative robots or cobots, but “Intelligent Assist Device.”
Colgate and Peshkin would go on to create their own company, Cobotics, to produce the first cobots used in the manufacturing industry. They were used in an automobile company’s final assembly line. The company was bought by Stanley Assembly Technologies in 2003. Since then, other companies have gone on to develop different types of collaborative robots to meet the demands of various industries.
The International Federation of Robotics (IFR) classifies robots into two types: robots used in manufacturing, and those used for domestic and professional purposes. Most collaborative robots fall under the first types.
Like other machines used in manufacturing and industrial uses, collaborative robots have different applications depending on factors like their adaptability, size, mobility, and safety features. This helps streamline the process of producing manufactured foods by using machines to make certain processes faster, also known as the concept of automation.
Humans can do most of the tasks in a production line, but many robots today were invented to do certain tasks faster and more efficiently. However, while studies suggest that around 8.5% of manufacturing positions will be automated by 2030, there are just some tasks that require both human and robots. Given that a lot of robots’ processes aren’t safe to work with humans (e.g. sharp metal edges, fast movement, machine temperature), there’s a growing need for cobots.
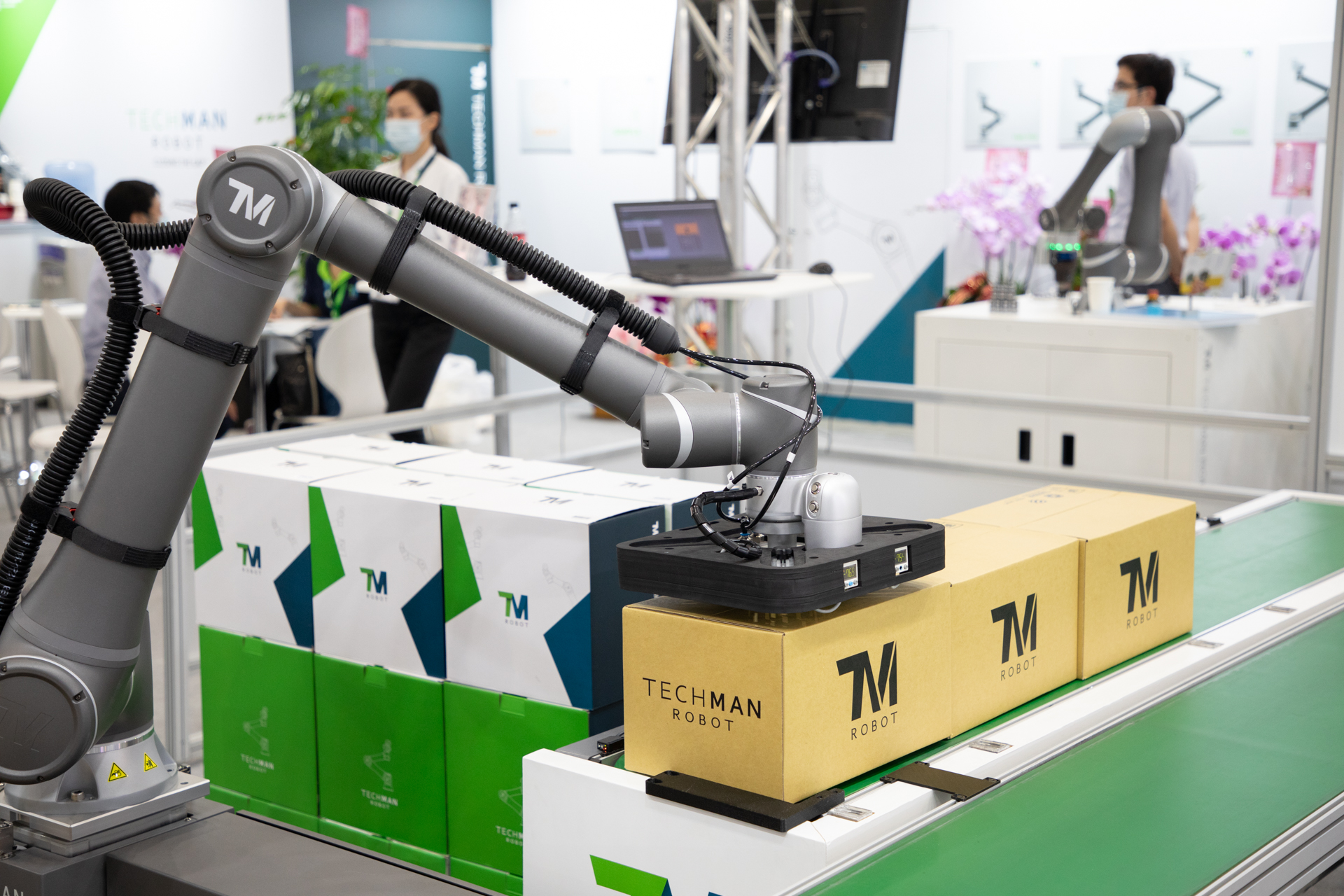
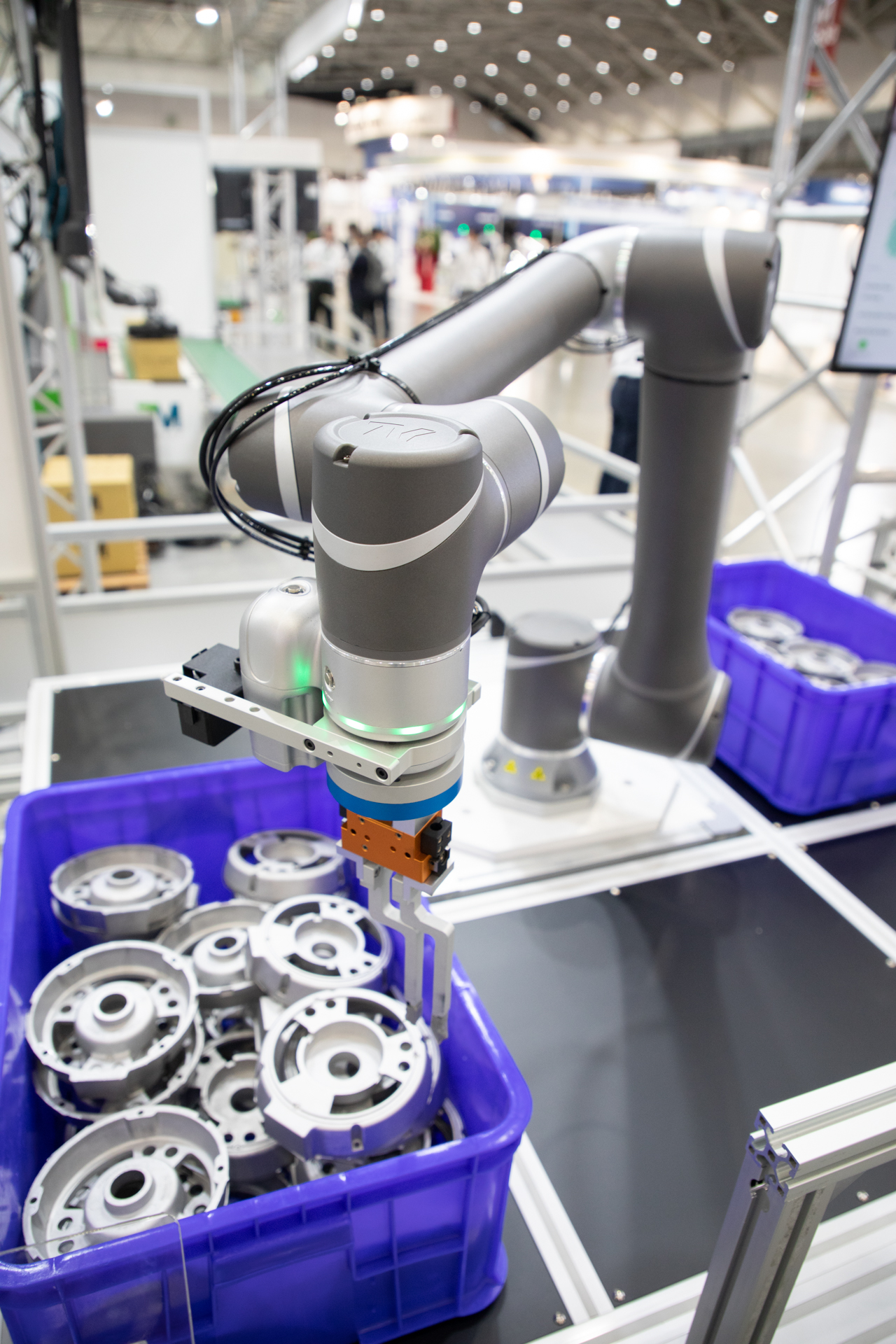
Collaborative robots are mostly used in logistics (moving and carrying heavy loads), manufacturing (assembly, welding, painting), and industrial purposes, but they’re also used for other applications. Cobots can be used by consumers or for public use such as serving as information robots or serving as moving security patrol in guarded facilities. This takes care of the more minor steps to production and operation and making it faster for human labor to handle the more complex processes robots can’t do (for now, at least). Some of their tasks include:
- Full logistics process – picking, sorting, and packing goods, avoiding injuries associated with heavier loads or dealing with dangerous products that have safety risks.
- Quality control – collaborative robots can work for a prolonged period of time with consistent performance while minimizing human error. This ensures a standard level of quality on the manufacturer’s part.
- Machine tending –cobots can replace human workers in repetitive and potentially dangerous work of loading and unloading parts from a milling, brake press, CNC, plastic molding, or other machines. Also improving production capabilities such as product output, quality, and consistency.
Like ordinary industrial robots, collaborative robots can work both on its own, before, or after a human finishes their task, or alongside a human.[/vc_column_text][vc_video title=”Quality control of a SSD production line using cobot to help run performance tests” link=”https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DVnFT9audks”][mk_padding_divider][vc_column_text css=”.vc_custom_1582780501241{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
Collaborative Robots for Manufacturers
Robots have become a ubiquitous feature in manufacturing, especially in established corporations and large companies looking to streamline their operations, make their processes more efficient, and reduce costs on manual labor. However, this puts small to medium enterprises at a disadvantage because they couldn’t afford the costs of building and coding their own robots.
This is why collaborative robots have become a major game-changer in the manufacturing industry. A business with the resources can opt to create their own cobots from scratch, but for the most part, collaborative robots are becoming an actual product in the B2B market. Robotic companies that produce cobots provide the materials and coding, making it more accessible to smaller businesses.
This makes it easier for smaller businesses to begin automating some of their processes. Without automated processes, some of the more menial and back-breaking jobs are left to human labor, which can not only be demotivating but also put a business’ people at risk for both injuries and long-term effects on the body.
Benefits of Automation with Cobots
- Advanced automation with reduced costs
- Cobots give manufacturers for medium-sized businesses access to advanced automation without the high costs of programming and constructing robotics that may still post a safety risk to human labor within the manufacturing process. Collaborative robotsare also easierto program than traditional robots, lowering coding efforts from your employees.
- Flexibility
- Collaborative robots are generally smaller and more portable than traditional robots, so they can have multiple purposes throughout the production line without any hassle transporting it. Aside from their hardware, their programming can also be considered flexible, so cobots can be repurposed for different uses.
- Safety
- Collaborative robots are designed with humans’ safety in mind, so they can be work right next to humans without the risk of injury. They can move slower when necessary and apply less force, which makes them less of a risk in a manufacturing center.
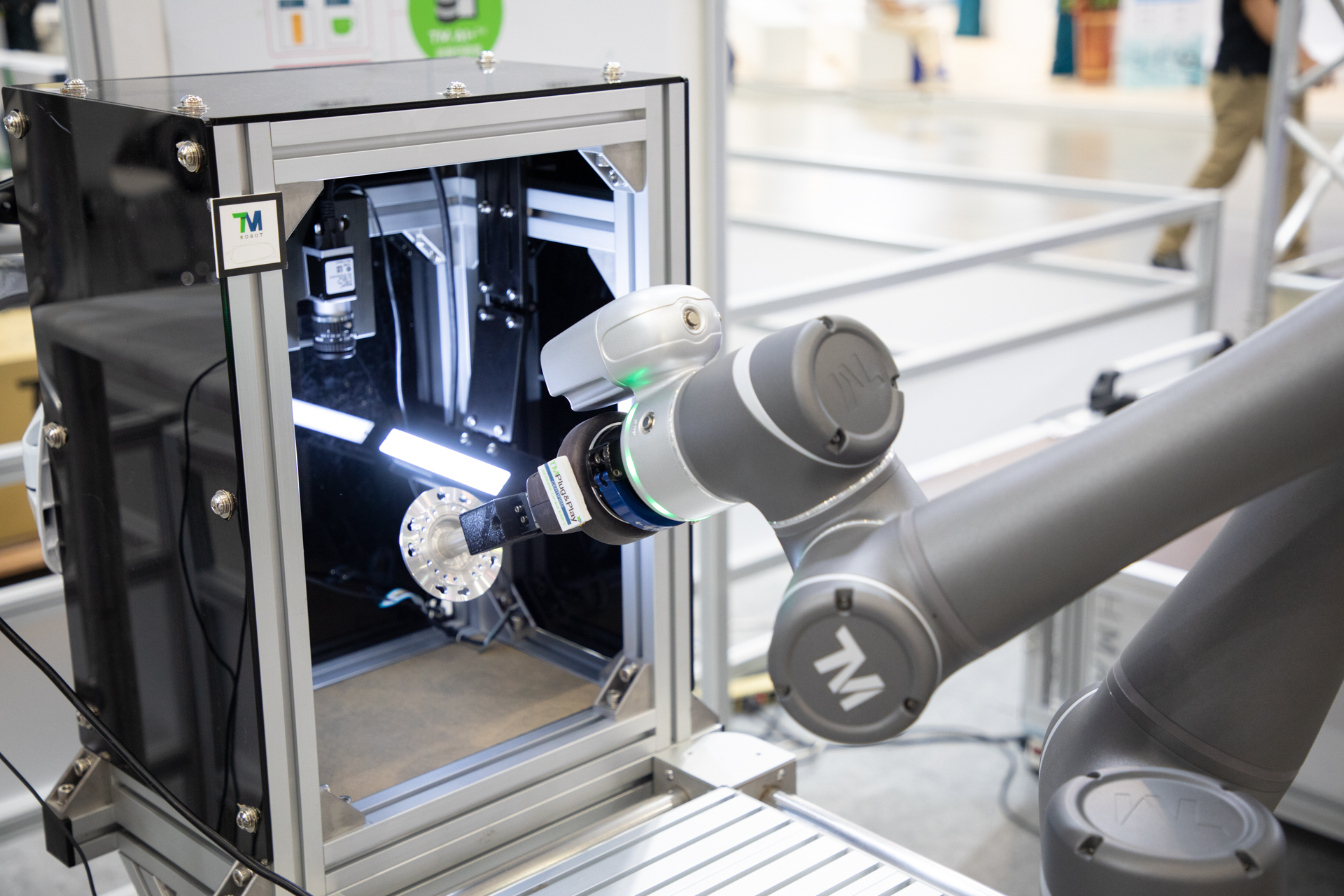
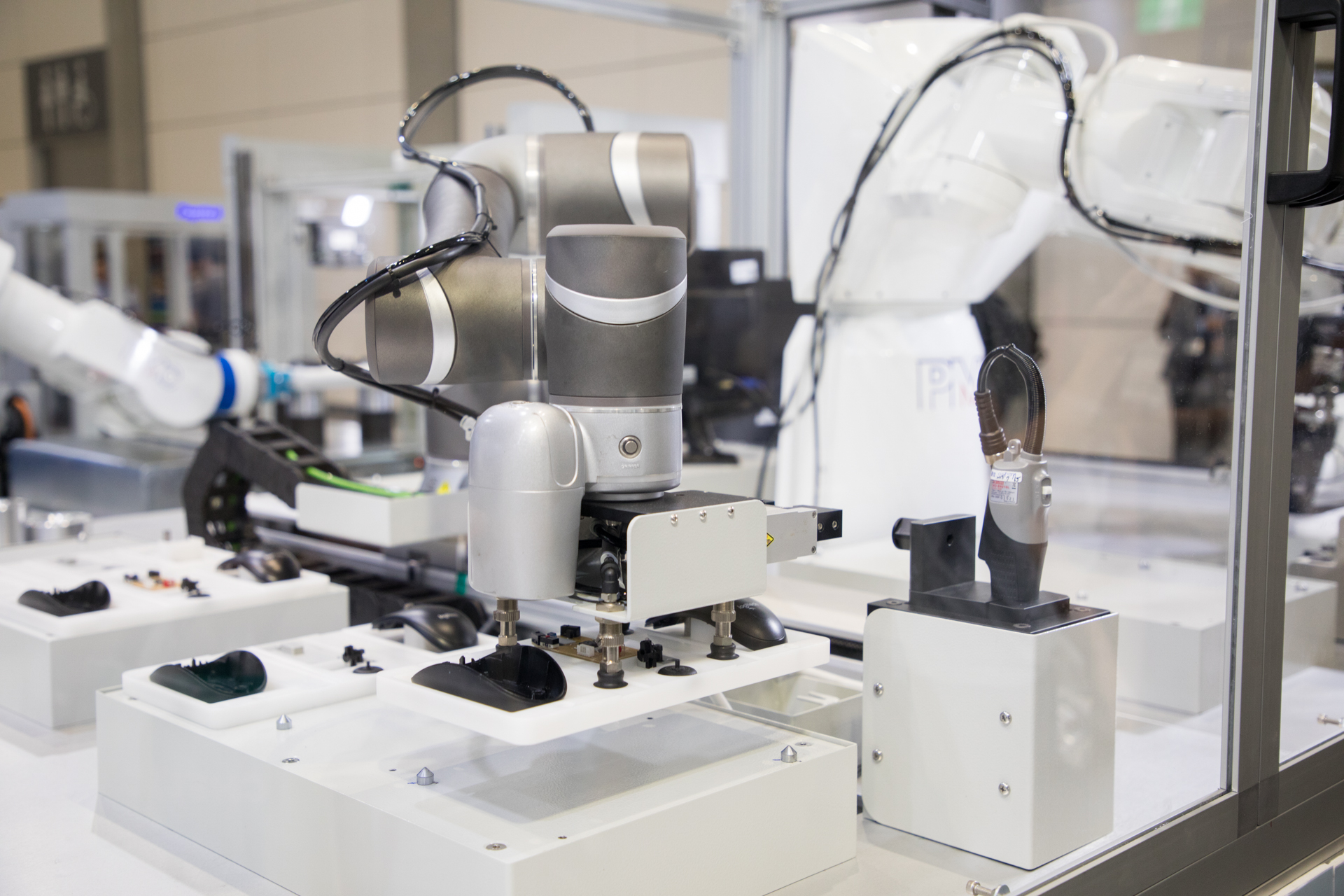
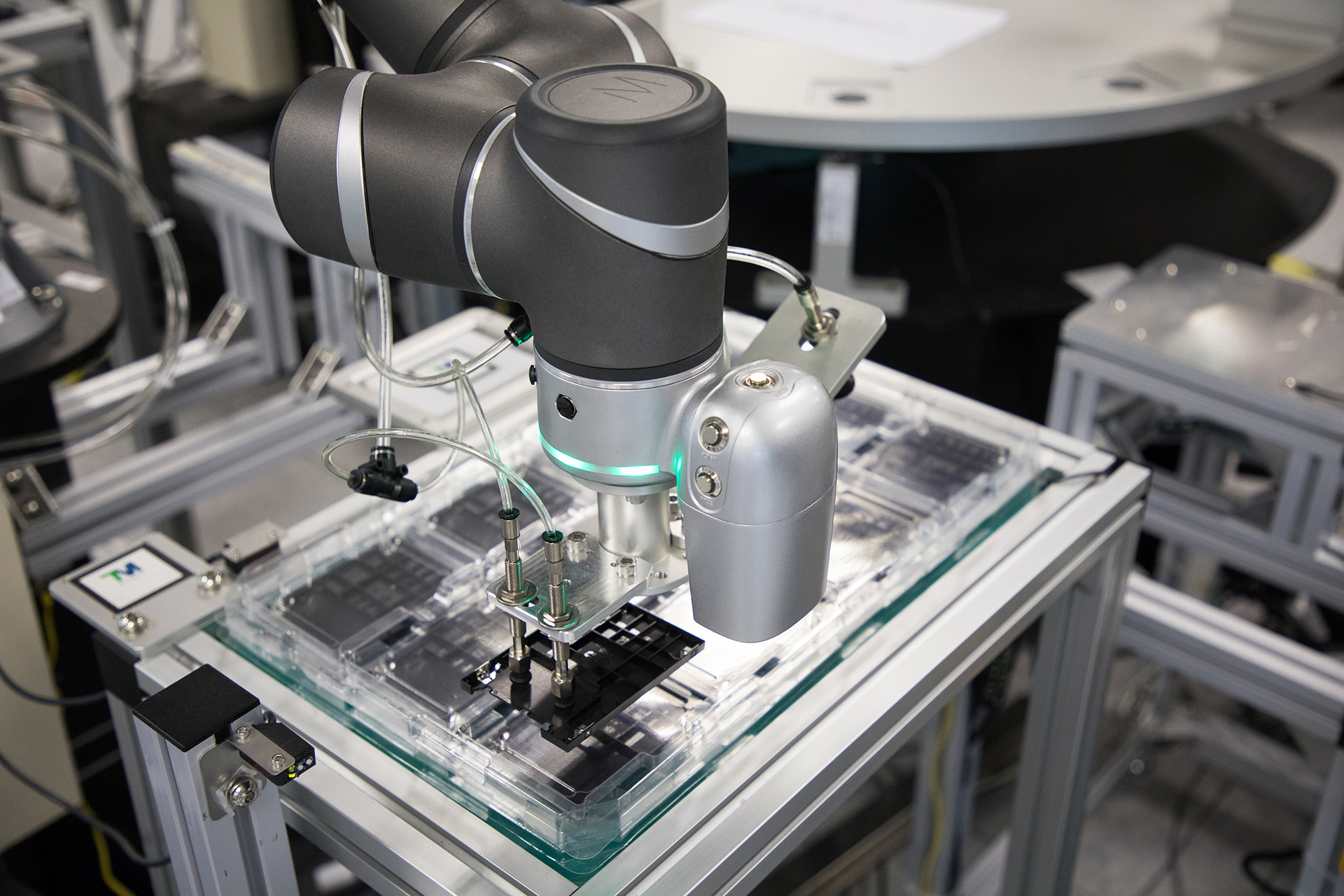
Robot Vision System
Some cobots are built with sensors and cameras, with at least one mounted on its robotic arm serving as its “eye”. This set-up allows a cobot to have a sort of “vision system” and get as much visual data as needed to perform certain tasks with humans.
A cobot’s camera takes 2D or 3D scans of the object, which is then stored in its database. When a cobot detects that it’s holding the same object, it can be triggered to perform the appropriate task. Once complete, it can be installed on an assembly line.
A robot vision system has three parts. While this may seem like a long process, the entire thing takes place within less than one second.
Image Capture
The collaborative robot captures footage of an object within its line of sight, depending on how the assembly line is structured. After it starts to capture visual data from a certain calculated distance, the cobot will analyze the images, and enhance it for a clearer picture to work with.
Image Processing
After the images have been captured and saved into the collaborative robot’s database, it will be processed and analyzed down to the last pixel. Its artificial intelligence is responsible for comparing colors, shapes, and anything to connect it to the images programmed in the database.
Connectivity and Response
Once the machine recognizes and matches the object based on the pictures saved onto its database, it will perform the corresponding action pre-programmed.[/vc_column_text][vc_video title=”TM Robot performs an automated optical inspection of electronic components on the conveyor with its built-in vision system” link=”https://youtu.be/9v5WRg0VaIU”][mk_padding_divider][vc_column_text css=”.vc_custom_1582536099736{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
Robot Vision AI Benefits
One of the advantages of having a collaborative robot is its camera allows it to have a “vision.” And, with its artificial intelligence, it is possible for a collaborative robot to do a number of things using its vision.
Increased Efficiency
Just because a collaborative robot operates based on the images it’s saved does not mean its process is too restrictive to create different designs. Programming a cobot’s AI vision means that the scope can be tweaked to allow for different designs and variations of a product as long as some of its features are similar. This is ideal for products that have different colors or styles but the same shape and size.
Ensure Product Consistency
Ensuring consistency for all items in the production line can be exhausting for human workers, since this means one person checking multiple items for consistency throughout the entire production process. This is extremely repetitive, and even then the task may be prone to human error. Cobots, however, can do the same task over and over without the strain or faltering quality over time.
Increased Reliability
Compared to other robots that do not have AI or robot vision, collaborative robots are generally more reliable because they’re not going at their tasks blindly. They’re basing the process of their operations based on saved visual data and how the object they’re working with looks. If something doesn’t look up to par, they can skip that object, saving time, quality, and resources (why waste raw materials on something that doesn’t measure up quality-wise?) while also issuing quality control on products.
Safe Working Environment
Robots move at directions and speeds they were programmed to move. Ordinary robots do not have safety measures, so it cannot detect if something is in its way unless that object is strong enough to stop it. This means that if a human accidentally got in the way of its operations, that robot won’t stop, which could be dangerous for the human involved, hence the reason why regular robots are kept away from human workers.
In comparison, collaborative robots are built with safety in mind. Their sensors and cameras can detect obstructions blocking their way, which make them stop or slow down. This makes them much slower in a productive sense, but much safer if you’re looking to decrease the risk of on-site accidents in the production line.
Reduced Operating Costs
A collaborative robot is a major investment for your business. This is in terms of time saved, higher productivity, consistent product quality, and higher employee morale. These can all contribute to lower operating costs.
Collaborative robots are paving the way for streamlined, efficient, and consistent products off the production line. In a time where technology is available to improve your operations, why settle for the chance of human error or the risk of your employees getting injured or burned out from menial everyday tasks that technology can handle safely and efficiently?
Contact Techman Robot today to find out more about our collaborative robots and automation solutions to improve your business.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column][/vc_row]