[vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1575398325680{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 100px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text css=”.vc_custom_1595423245181{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
Without robotic vision, robots are blind machines that move according to their programming. They rigidly follow the code that dictates their functions, making them ideal for repetitive tasks that could be physically draining and challenging to people. Now that we are at the advent of Industry 4.0, robots are also evolving. It will allow them to keep up with the demands and trends of the fourth industrial revolution.
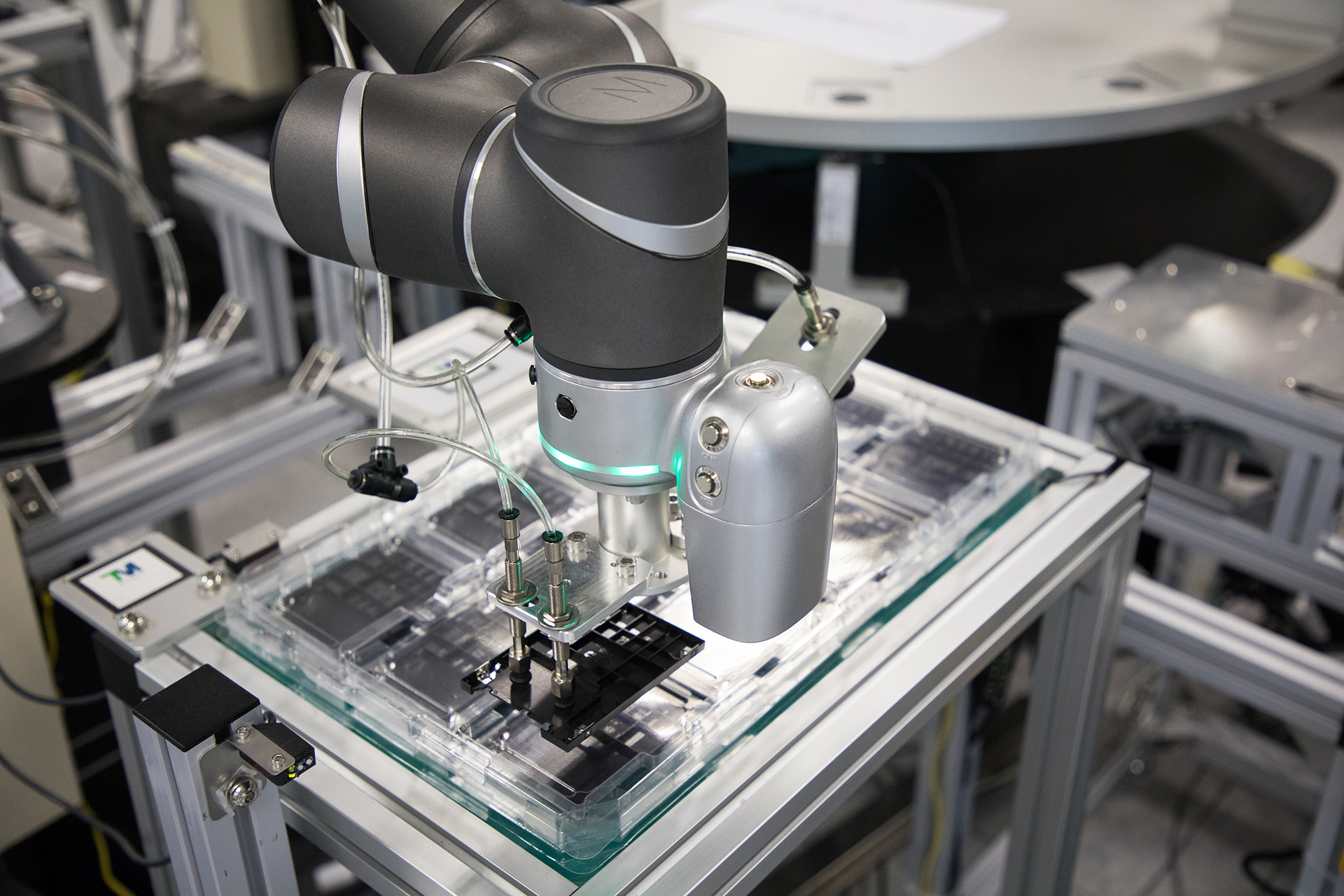
Central to the evolution of robotics is the creation of a robot vision system for collaborative robots. Machine or robot vision is a key feature of this evolution, introducing new levels of precision and accuracy in smart automated processes.
Vision systems help cobots perform tasks such as inspecting, identifying, counting, measuring, or reading the barcode. Ultra-high-speed imaging and lens quality facilitate multi-operations in one process.
Machine learning is also being applied to robotics, teaching collaborative robots to perform new tasks based on data patterns. It gives vision robots sophisticated search and corrective movement skills, such as the elimination of overlaps, distortions, or misalignments.
Vision systems, however, are also useful in non-robotic functions. They can be placed in critical production floor locations such as conveyor lines to aid with product quality control reviews.
At present, most robot vision systems are used for materials handling and removals. See examples of these varied robot vision applications at Techman Robot.
Giving robots the ability to see is a game-changer. The ability to perceive their immediate surroundings significantly enhances cobot capability, which in turn benefits human workers, companies, and industries at large. We understood this early on at Techman Robot, motivating us to integrate built-in vision systems in our TM Robot Series of collaborative robots.
In practice, introducing vision-guided robots or cobots with robot AI vision into your manufacturing system makes sense if they can be easily configured and operated by your staff, saving you time and labor costs.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row fullwidth=”true” fullwidth_content=”false” css=”.vc_custom_1575398477979{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 100px !important;background-color: #444444 !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”12616″ img_size=”400×400″ alignment=”center”][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][mk_fancy_title tag_name=”span” font_family=”none”]
How Does Robotic Vision Work?
[/mk_fancy_title][vc_column_text align=”center” css=”.vc_custom_1575399043701{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
Cobots “see” via one or more integrated cameras. At least one robot vision camera will be mounted on the robotic arm itself, literally serving as the eye of the machine. In some cases, additional cameras are installed in strategic locations in the cobot’s working cell. This set-up allows the camera to have a wider visual angle and capture as much visual data as it needs to perform its function in collaboration with human workers.
Before the machine is deployed, it is first programmed and taught to identify the objects with which it should interact. The cobot’s camera will take 2D or 3D scans of the object. The image will then be stored in the cobot’s database and programmed to trigger the machine to move and perform specific tasks.
Once the programming is complete, the cobot can finally be installed in the assembly line.[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text css=”.vc_custom_1575398734852{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
The Process
There are three segments in a robot vision system:
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][mk_icon_box icon=”mk-icon-caret-right” title=”Image capture” font_weight=”bold” style=”simple_ultimate” title_color=”#ffffff” txt_color=”#ffffff”]The cameras capture footage of the objects that enter a cobot’s workspace. If the set-up is halfway through the assembly line, there is a good chance that conveyor systems will deliver the products directly before the cobots. The camera/s will start capturing visual data from a calculated distance. Afterward, the machine will analyze the images or footage and enhance it to produce a clear picture.[/mk_icon_box][mk_icon_box icon=”mk-icon-caret-right” title=”Image processing” font_weight=”bold” style=”simple_ultimate” title_color=”#ffffff” txt_color=”#ffffff”]The picture will go through further processing and analyzed by pixel. The system will compare the colors and apparent shape of the object with the image programmed in its database.[/mk_icon_box][mk_icon_box icon=”mk-icon-caret-right” title=”Connectivity and response” font_weight=”bold” style=”simple_ultimate” title_color=”#ffffff” txt_color=”#ffffff” txt_link_color=”#ffffff”]Once the machine recognizes that the object in the picture matches the pre-programmed image, it will perform a corresponding action onto the object before it.[/mk_icon_box][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_column_text css=”.vc_custom_1575401271137{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
This entire process happens in quick succession within seconds.
To put things into context: one good example of this process would be a robot vision system for the icing and decorating line of a cake factory. Two custom cobot arms are stationed on either end of this assembly line: one spreads buttercream frosting on the entire cake, while the other pipes complex icing designs on top.A conveyor belt brings in the cakes and gets them frosted first before conveying them to the decorating arm (meanwhile, the frosting arm gets started on the next cake).
Both arms have cameras (eyes) that scan each cake that comes before it. Every time the frosting arm registers an un-iced cake, it releases its icing nozzle and scraper, which spreads the buttercream evenly on the top and sides of the cake. The same goes with the decorating arm: the sight of an iced cake, whose frosting matches the image of the model cake programmed into its system, would trigger the machine to create the corresponding icing design.
In this scenario, the cake factory can mass-produce cakes with impressive speed and precision. The cobots in this factory are clearly recipe-driven, which means the bakery can easily change cake designs or even produce more than one cake style from a single decorating line.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][vc_column_inner width=”1/2″][vc_single_image image=”9863″ img_size=”500×500″][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row][vc_row css=”.vc_custom_1575401856828{padding-top: 100px !important;padding-bottom: 100px !important;}”][vc_column][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][mk_fancy_title tag_name=”span” font_family=”none”]
The Advantages of Robot Vision AI
[/mk_fancy_title][vc_column_text css=”.vc_custom_1575401514755{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
The above is a basic demonstration of how cobots enhanced with vision systems can fit into an assembly line. The example also gives us a clear idea of their benefits:
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][mk_icon_box icon=”mk-icon-check” title=”Increases efficiency” font_weight=”bold” style=”boxed” icon_color=”#ffffff”]Robot vision camera can help take images for your own AI model training, and the image data can be automatically collected. The training module can then be used in factories for robots to better identify various kinds of product defects.[/mk_icon_box][mk_icon_box icon=”mk-icon-check” title=”Ensures product consistency” font_weight=”bold” style=”boxed” icon_color=”#ffffff”]Human workers are capable of icing a cake, but it would be unrealistic to expect anyone to be consistently precise for six to eight hours straight. This is an example of repetitive tasks for which robots are an excellent replacement. And with robot vision, factories can be more flexible in these assembly lines and take advantage of the visual recognition feature. They can produce more if they allow cobots to react to the variables that enter their fields of vision.[/mk_icon_box][mk_icon_box icon=”mk-icon-check” title=”Reliable” font_weight=”bold” style=”boxed” icon_color=”#ffffff”]Vision-guided robots are more reliable than their non-seeing counterparts. They don’t function blindly, after all. If something vastly different from the 2D or 3D images programmed in the system comes across their path, they can be made to skip that object and move on to the ones that pass this first level of quality control. In this respect, factories can boost efficiency with the use of their raw materials or parts in the assembly line.[/mk_icon_box][mk_icon_box icon=”mk-icon-check” title=”Promotes a safe workplace” font_weight=”bold” style=”boxed” icon_color=”#ffffff”]Traditional, automatic machines move at directions and speeds per their programming. Put a human worker on its path, and it will still keep going, regardless if they get out of its path or not. Cobots with robot vision AI, on the other hand, have sensors that detect obstructions along their pre-programmed paths and movements. They stop at once their sensors register an object in the way instead of powering on at full speed. With vision-guided cobots, factories can reduce the risk of on-site accidents significantly.[/mk_icon_box][mk_icon_box icon=”mk-icon-check” title=”Reduces operating costs” font_weight=”bold” style=”boxed” icon_color=”#ffffff”]Cobots with robot vision systems constitute a major investment. Although returns on any form of investment are never guaranteed, enterprises can be sure of gains, such as time and resources saved, higher production rates, better and consistent product quality, and better-rested employees. In time, the returns can manifest as lower operating costs and increasing sales.[/mk_icon_box][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][vc_row_inner][vc_column_inner][vc_column_text css=”.vc_custom_1575401917424{margin-bottom: 0px !important;}”]
As a creator, designer, and innovator of collaborative robots and application software, we have witnessed clients reap these benefits after integrating vision-guided cobots into their factories. These companies are from the industrial and manufacturing sectors as well as industries where the need for automation is moderate but highly beneficial.
Explore the possibilities for growth that robot vision software can bring to your business. The earlier you do it, the bigger your head start against your competitors.
[/vc_column_text][/vc_column_inner][/vc_row_inner][/vc_column][/vc_row]