Background and Customer Needs
Our client, a well-known electronics manufacturer in Taiwan, specializes in high-volume server production. In the final stage before shipment, every unit must undergo visual inspection to verify the presence, positioning, and condition of key components—such as connectors, cable ties, caps, battery, cable routing, SSDs, and screws.
Previously, this process relied heavily on manual inspection, which was not only time-consuming but also inconsistent due to worker fatigue. The increasing complexity of server configurations further amplified the risk of undetected defects, quality variations, and costly rework.
The customer required a reliable and scalable inspection system that could:
- Perform consistent visual checks across multiple component types
- Reduce human error and inspection time
- Ensure stable quality before delivery
Challenges
Although SOPs were in place, the manual inspection process faced the following key challenges:
- Fatigue-related errors: Human inspectors often missed subtle issues, especially during long shifts.
- Lack of consistency: Judgment varied between operators, impacting quality stability.
- Non-traceable process: No systematic method existed to record or trace inspection outcomes.
- Complexity of components: The wide range of parts and configurations made visual checking difficult to standardize.
These issues underscore the need for an automated solution that could ensure repeatable accuracy and reduce dependence on manual labor.
Solution
To improve inspection performance, the manufacturer implemented a robotic arm solution using the TM AI Cobot, which is integrated with a built-in vision system, and a powerful software called TM AI+ Trainer.
Inspection Process:
- The AI model was trained using image datasets labeled as “OK” and “NG” based on multiple server component samples.
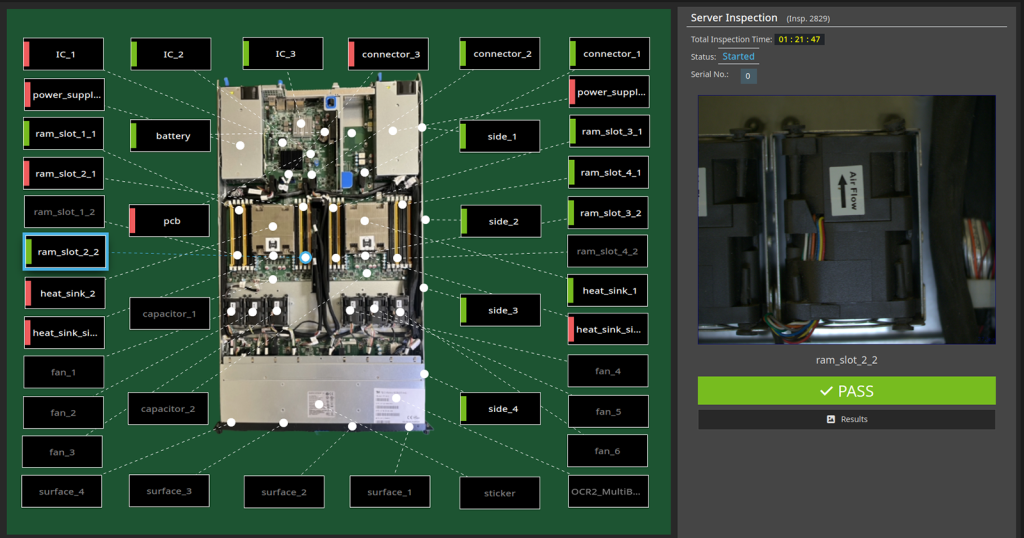
- After capturing an image of the server, the AI model classifies each area (e.g., connector, battery, cable tie) to determine whether the part is present, correct, or abnormal.
- If an abnormality (NG) is detected, the system immediately flags the unit and removes it from the line for further handling.
Key Inspection Targets:
- Connector, cap, and cable tie detection
- Battery presence and cable routing
- SSD and screw presence verification
AI Model Training
- AI Function Used: Classification
- Data Source: Labeled images captured directly from production
- Training Method: Standard supervised training with categorized image sets

Results & Benefits
- Parallel multi-point detection: Simultaneous inspection of multiple parts reduced cycle time
- Higher consistency: AI provided uniform inspection judgment regardless of shift or operator
- Improved traceability: All inspection results were recorded digitally for tracking and QA analysis
- Reduced rework and after-sales risk: Only qualified servers proceed to shipment
Conclusion
With TM AI Cobot as an automated inspection solution, the customer successfully replaced time-intensive manual checks with a reliable AI-powered system. This not only enhanced inspection efficiency and traceability but also ensured higher product quality at the final stage—reinforcing trust in the company’s server manufacturing excellence.